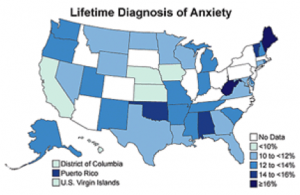
Anxiety is one of the most common mental health problems in the U.S. According to the U.S. National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), just over 18 percent, or about 40 million American adults aged 18 and older, have an anxiety disorder. According to the CDC, depression and anxiety are two major causes of illness and death in the United States. Females were more likely to be diagnosed with depression (20.2% vs. 8.2%) and anxiety (14.3% vs. 8.2%) than were males.
Anxiety is a normal response to stress that is part of human physiology. It can however fall out of balance and become a chronic, disabling disorder. Currently, anxiety has been categorized into five major types: Generalized Anxiety Disorder, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder, Panic Disorder, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Social Anxiety Disorder. The symptoms people experience include fear, panic, shortness of breath, palpitations, dry mouth, sweaty palms, nausea, muscle tension and dizziness.
What are the Causes of Anxiety?
- Stress
- Caffeine
- Sugar
- Nicotine
- Alcohol
- Drugs
- Nutrient deficiencies
- Heavy metal toxicities
- Disturbed sleep
- Food allergies
- Environmental toxins
- Thyroid problems
- Low blood sugar
- Adrenal health-issues
- Simple carbohydrates
Low Cholesterol
The BBC news reported in 1999 that women with a low cholesterol level may be approximately twice as likely to suffer from depression or anxiety problems. 1 Writing in the journal Psychosomatic Medicine, psychologist Dr. Edward Suarez noted, “There is now a compelling body of evidence in both men and women that low cholesterol is a potential predictor for depression and anxiety in certain individuals.” If levels are below 150 mg/nl, your cholesterol may be too low.
Magnesium Deficiency
Almost 80% of Americans are magnesium deficient. Multiple studies have found that a magnesium deficiency is linked to anxiety and depression. 2,3
An interesting link from this chart is that West Virginia has very poor soil (low in calcium and magnesium) and has one the highest rates of anxiety.
Lack of Omega- 3 Fatty Acids
A research team from Harvard University has reported that eating fatty fish can help lift depression. Fatty fish such as salmon and cod contain omega-3 fatty acids which are believed to raise levels of the brain chemical serotonin in a way similar to anti-depressants like Prozac.
Chronic Simple Carbohydrate Consumption
Excess of consumption of simple carbohydrates in the form of refined sugar and grains deplete serotonin (feel good hormone) stores and deplete B-vitamins required to convert amino acids into many neurotransmitters. What are simple carbs? Anything flour based including chips, crackers, tortillas, muffins, bagels, bread etc.
The Gut Brain Connection to Anxiety
According to Dr. Emeran Mayer, a professor of medicine, physiology and psychiatry at the UCLA, “the majority of patients with anxiety and depression will also have alterations of their GI function.” What’s interesting is that 95% of serotonin is housed in the gut, where the majority of communication occurs within the digestive tract; 90% of this information will be translated to the brain. The messages can be positive, but they can also be unpleasant. Many of us have experienced the feeling in our gut right before public speaking or other traumatic emotional circumstances. This disrupts digestion and creates a feeling of anxiety, uneasiness and sometimes panic. Any damage by the diet to the gut will also send negative signals to brain, manifesting as anxiety, brain fog, irritability and depression.
Link between Gluten and Anxiety?
Speaking of brain fog, that leads us to gluten. In gluten sensitive individuals, gluten can actually shut down blood flow in to the frontal and prefrontal cortex, the part responsible for focus, managing emotional states, planning, organizing, consequences of actions, and our short term memory. This process is called “hypoperfusion” and is strongly associated with ADHD, depression and anxiety.
MAO-A, MTHFR 1298 and COMT
If you have certain variants in MAO-A, MTHFR 1298 or COMT, you are more prone to anxiety. Genetic testing can help find out if you require more magnesium, vitamin C, folate, B2 and B12 to normalize enzyme function and decrease anxiety.
Exercise
The effects of exercise on helping depression and anxiety are well documented. The type of exercise will vary with the individual. Many people find yoga and walking to help relieve the symptoms of anxiety and depression. If you have a dog, you can see the effects when he hasn’t been walked. He may get anxious, depressed and destructive; but take him for a long walk and you will see a very different dog. We need to treat our bodies in a similar way and use them for what they were designed to do; move!
For an in-depth analysis of mental health, see Alex Swanson’s article Mental Health Starts in the Gut, Not the Brain.
Recommended Supplements for Anxiety
You will not require all of the following recommendations. The best approach is to identify the key root causes of anxiety, and target the nutrients most needed. For example, if digestive issues are present, probiotics and magnesium are going to play a very important role. If you don’t eat eggs or liver, choline will be essential. If you avoid fish and low serotonin is an issue, cod liver oil. If you have high stress in your life and low dopamine, vitamin C and magnesium at the right dosages are key.
1. VSL #3 High Potency Probiotic Capsules
Are probiotics the new prozac? According to Dr. Amen, “When you combined published and unpublished studies of antidepressants, the treatments we have today are no better than they were 50 years ago.” New research from the peer reviewed Gastroenterology has found the first evidence that women who eat probiotic yogurt regularly had altered activity in brain regions that regulate emotions and internal body sensations. Taking a probiotic daily can ensure healthy populations of good bacteria. Make sure to eat prebiotic rich food like raddichio, garlic, onions and artichoke.
Magnesium deficiency is not something that can be measured by food recall questionnaires due to the fact that it has virtually disappeared from our water and top soil. Government studies say that 68% of people are magnesium deficient, however I would argue that percentage is actually quite higher. To activate vitamin B6, magnesium is required. So imagine how your mental health is affected by just low B6 and magnesium status. People with gastrointestinal issues, Type-2 diabetics, alcoholics and older adults all struggle with magnesium absorption on top of poor intake. It is involved in serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine production, is a major muscle relaxant and constipation remedy.
Vitamin C is required in high amounts by the adrenal glands, and by the brain to produce the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine. Over thousands of studies have found positive benefits of dosages over 500mg, and for anxiety 2-3,000 milligrams may be needed.
A large population-based study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, people with higher blood levels of choline had lower levels of anxiety. It is extremely common for women to be choline deficient, and is also why we are seeing an increase in gallbladder issues, non-alcoholic fatty liver and high homocysteine levels.
High quality vitamin A, D, EPA and DHA for proper brain and nerve function. Omega-3 fatty acids which are believed to raise levels of the brain chemical serotonin in a way similar to anti-depressants like Prozac.
People with anxiety often require more b-vitamins. B-vitamins are known as the “anti-stress” vitamins. People with anxiety often have elevated amounts of the anxiety-causing neurotransmitters including norepinephrine and epinephrine, with high estrogen. Niacin in particular helps because nicotinic acid is a cofactor for the COMT enzyme, which helps breakdown excessive amounts of norepinephrine, epinephrine and estrogen.
Studies have shown that the herb Ashwagandha has demonstrated the ability to relieve stress, protect brain cells, and to be as effective as some tranquilizers and antidepressant drugs without the side effects. In one study, oral administration of ashwagandha for five days suggested anxiety-relief similar to those achieved by the anti-anxiety drug Ativan and antidepressant effects similar to the antidepressant drug Tofranil.5
Sources:
1. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/352216.stm
2. Kirov GK, Tsachev KN. Neuropsychobiology. Magnesium, schizophrenia and manic-depressive disease. 1990;23(2):79-81.
3. Jacka FN, Overland S, Stewart R, Tell GS, Bjelland I, Mykletun A.Association between magnesium intake and depression and anxiety in community-dwelling adults: the Hordaland Health Study.
4. http://www.wvencyclopedia.org/articles/509
5. Bhattacharya SK, Bhattacharya A, Sairam K, Ghosal S. Anxiolytic-antidepressant activity of Withania somnifera glycowithanolides: an experimental study. Phytomedicine. 2000 Dec;7(6):463-
6. http://www.nytimes.com/2005/08/24/health/24iht-snbrain.html?pagewanted=all
7. Well Being Journal. The Grim Side of Grains. May/June 2012.